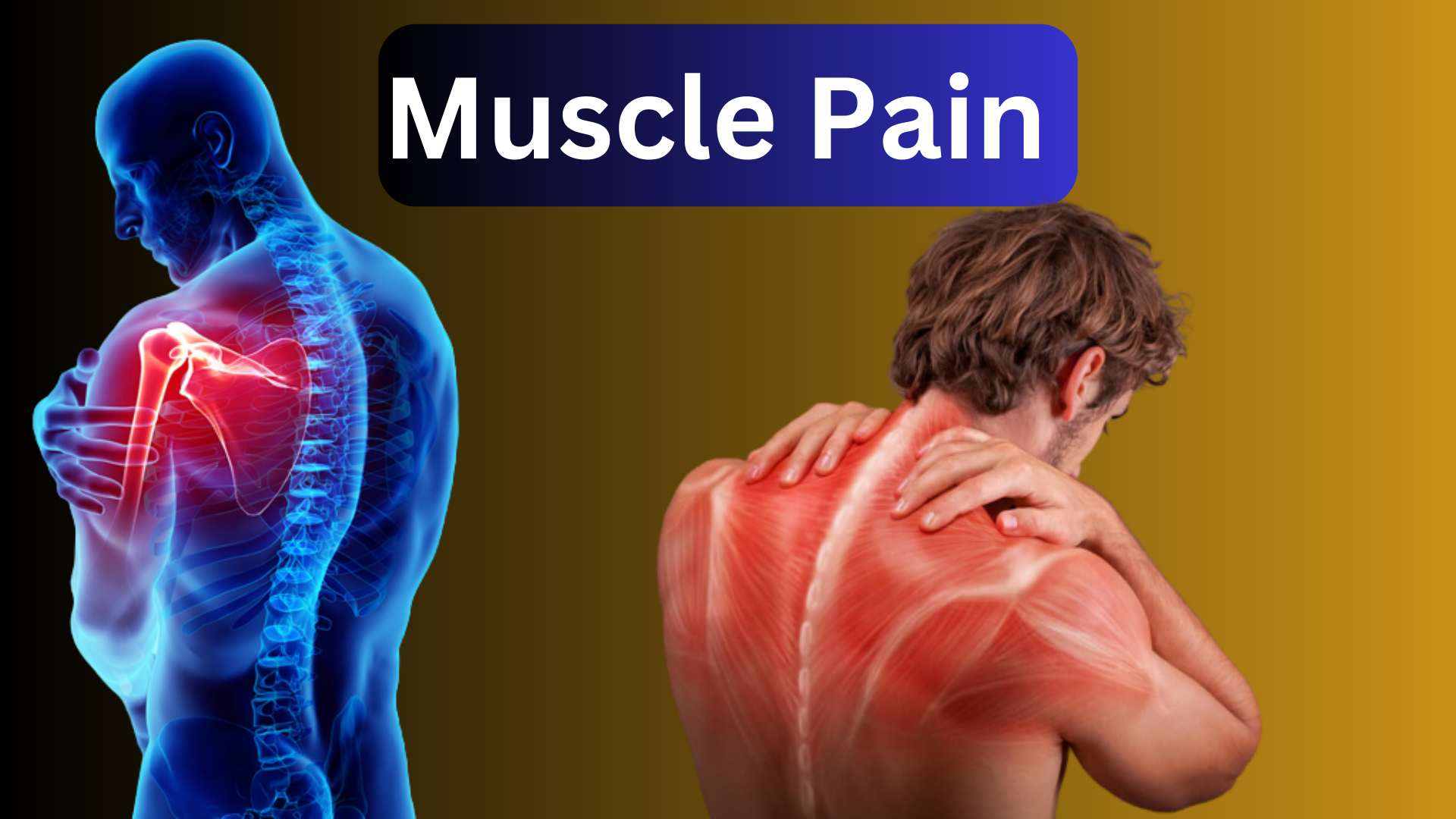
Muscle Pain (Chronic Soft Tissue Pain): Causes & Treatment. Click to learn back muscle strain, relief for lower back pain, pain in lower back right side, lower back pain left side, pulled muscle in back and many more.
Myalgia or muscle pain is a symptom of injury, infection, disease, or another medical issue. You can experience random discomfort feelings or constant, significant discomfort.
While some people only experience confined muscle pain, others experience common pain. Everybody feels pain in their muscles differently.
What is the Cause of Muscle Pain
The majority of the time, a muscular injury or strain from physical activity causes pain in the muscle. Muscle pain is also more common in athletes than in non-athletes.
Examples include muscle spasms, which are more severe forms of muscle stiffness, cramping, which is a brief and strong contraction of the muscles, and muscle tears.
These are a small breakage of the muscle and its surrounding envelope, pulled or strained muscles, which are large tears, and full-thickness muscle tears, which is the most severe kind of muscle tear.
Muscle discomfort may also be caused by a knock or impact, a pulled or strained muscle after moving unnaturally (as in torticollis or lumbago), a side effect from medication, or both. Similar to how tension in the muscles can cause pain, stress can also cause it.
Symptoms for Muscle Pain
While any muscle in the body can be affected, muscle pain typically affects the muscles in the arms, legs (Leg Pain), back, shoulders, stomach (Stomach Pain), and hips. Multiple signs can go along with this pain, including:
- Piercing pains
- Numbness
- Muscle rigidity
- Needles and threads
- A scorching feeling
- Stubby discomfort
- Inability to do particular actions without difficulty or discomfort
Swelling
Muscle Pain Treatments
While most discomfort, stiffness, and cramps are harmless, some muscle pain can be a sign of a more serious issue. As a result, the cause of the pain and the best course of treatment should be identified by asking a doctor.
Here is some best medicine that you can use on the recommendation of your doctor, it is the best to treat muscle-related pain, such as Pain O Soma 500mg, Soma 350mg and if you have chronic pain then Aspadol Er 200mg is the best medication.
Rest (a painful muscle should not be utilized), stretching or massaging the painful muscle, applying heat, and taking medications are typically sufficient for reducing the pain in cases of muscular soreness and stiffness.
If the pain is brought on by an injury, we advise using an ice pack, followed by rest, elevation, and bandaging of the injured muscle. Painkillers and muscle relaxants may be provided if the pain doesn’t go away.
Essential Oil for Muscle Pain
On multiple fronts, essential oils can provide relief: they can soothe the mind, uplift the heart, and ease pain.
It’s important to maintain your calm when you’re in pain. Your body experiences less stress when you can relax which gives your body more room to repair.
You may have minor muscle discomfort at the end of the day if you are always active and enjoy sports.
Getting a massage using oils that have anti-inflammatory, circulation-boosting, and detoxifying actions is the greatest method to treat muscle pain.
Nerve Pain VS Muscle Pain
Upwards of 20 million people get nerve pain, did you know that? The majority of people are unaware of the distinctions between nerve pain and muscle discomfort. This frequently results in ongoing problems or causes that are unknown.
It’s common for the reason for nerve pain to be unclear. Understanding their variations can help you manage your pain and enhance your quality of life.
1.) Muscle Pain
Muscle soreness and discomfort are frequently used together. You might categorize your pain either way, depending on how intense it is.
This kind of discomfort is typically brought on by an injury to one or more muscle groups. Because many people frequently can’t remember a specific circumstance where they injured one another, the term “injuries” is very vague.
It is usually a lot simpler to figure out what caused the injury if you are an athlete. For the vast majority of people, it is frequently more subdued.
2.) Nerve Pain
Nerve pain frequently gets confused with muscle pain while discussing different forms of pain. This form of pain results from nerve damage, but it is a little more complicated than a muscle strain.
The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system are two major categories of nerves that make up your body. Your brain and spinal cord both have nerves that are a part of your central nervous system.
Two parts of the peripheral nervous system work together to transmit motor and sensory information from the brain and spinal cord to the extremities. Any of these parts can sustain damage.
Will muscle pain go away?
People of all fitness levels can experience it, especially after trying a new sport or exerting themselves a little more than usual. Usually, the pain in your muscles will go away in 2 to 5 days, and you won’t need to see a doctor or any medication.
Are muscle pains normal?
Muscle discomforts are common, especially if you exercise rarely or are active. If your muscles start to pain, pay attention to your body and stop what you’re doing. In order to avoid muscular injuries, ease into new activities.
What helps muscle pain go away?
Try gentle stretching to help with muscle tightness.
- Massage of muscles.
- Rest.
- Ice can be used to lessen inflammation.
- Heat might aid in boosting blood flow to your muscles.
- A no-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) like ibuprofen (brand name: Advil), is available over-the-counter (OTC).
Where does muscle pain start?
The most frequent causes of muscular discomfort are stress, overuse, or muscle damage from physical activity or heavy jobs. Specific muscles are usually considered, and the pain usually begins during or immediately after the activity.