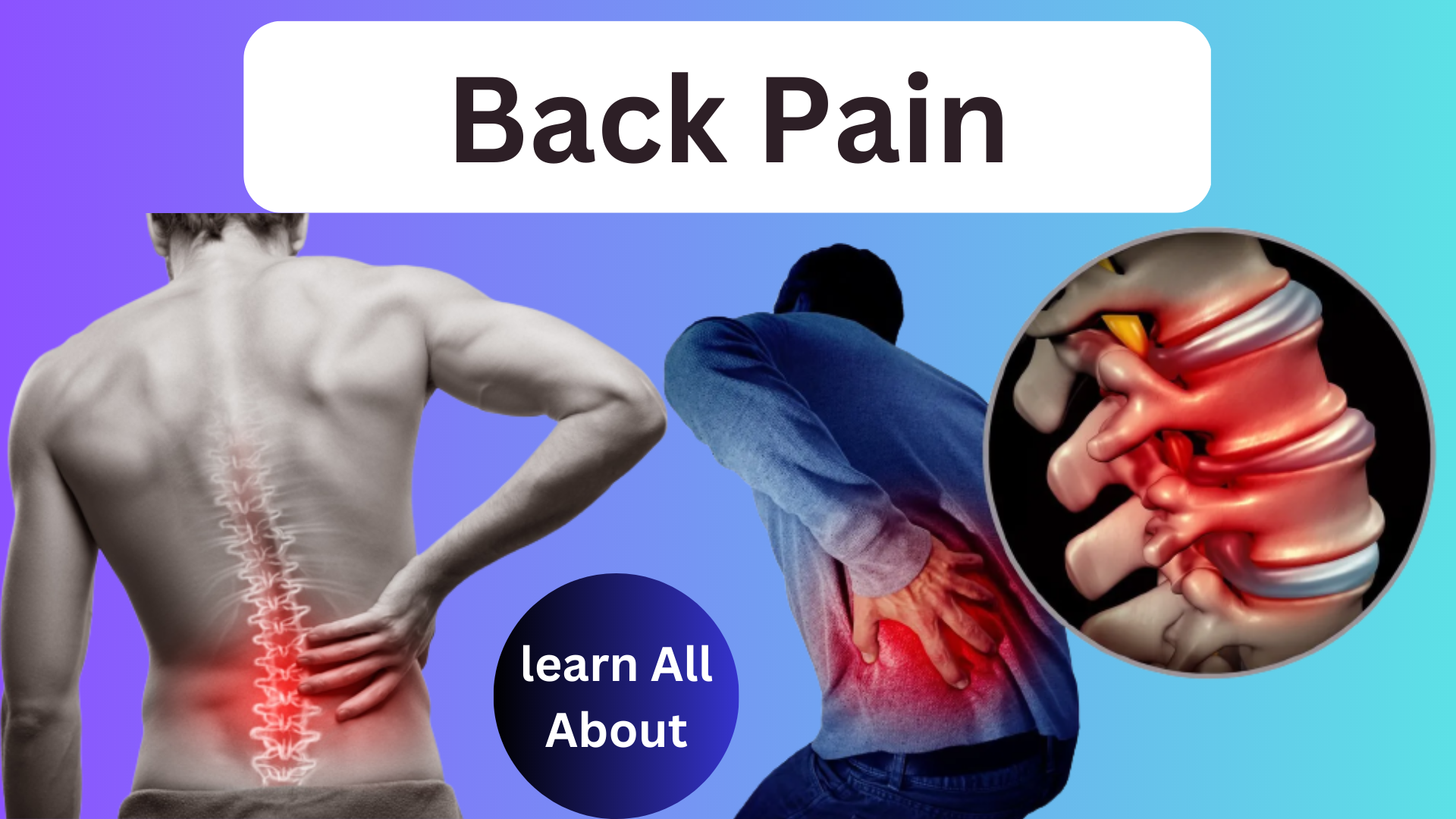
Most people will continue lower back discomfort at some point in their lives. Back pain that is mechanical in nature makes up about 97% of cases and is promptly healed.
However, other possible causes must be taken into consideration right away because many of them call for extremely specialized nonsurgical or surgical treatment.
The success of the particular therapy chosen for each patient will be maximized with careful, early attention to acquire the accurate diagnosis.
What is Back Pain?
Your lower back’s lumbar spine, which supports the weight of your upper body, is extremely important. It also controls everyday movements like bending, twisting, and coordinating the muscles in your legs, feet, pelvis, and hips.
Symptoms of lower back discomfort include:
- Continuous dull pain in your hips or pelvis.
- Muscle stiffness or spasms.
- Sciatica is a sharp, tingling pain that begins in the lower back and radiates down one leg.
- Pain that gets worse when sitting and rapidly gets better when moving around.
- Morning pain that is noticeably worse.
What Are The Causes Of Lower Back Pain?
Mechanical issues are the primary cause of back pain in the vast majority of patients. They may suffer a herniated disc due to stress on the spine’s bones and tissues or spondylosis (spinal osteoarthritis).
A potentially painful degeneration of one or more spinal joints(Learn about joint pain), as a result of hard lifting or twisting, a violent jolt in a car accident, or one of the other causes mentioned above. These are typical reasons for low back pain:
- Mechanical or functional damage.
- Active infection
- Inflammation
- Neoplasms (tumors)
- Referred pain, which is pain that arises in one place but presents in another, for example, discomfort from a kidney stone that radiates to the lower back or the belly.
Doctors must take into account the complete range of potential underlying problems, including inflammatory disorders, fractures, infections, as well as some serious conditions unrelated to the back that radiate pain to the back, in order to select the safest and most successful therapy.
When Are Diagnostic Tests For Lower Back Pain Necessary?
X-Rays:
- Patient is over 50 years old
- History of malignancy
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Increased ESR trauma
- Motor deficit
These symptoms show patients who are more likely to have an infection, cancer, or a fracture and less likely to suffer from simple muscle strain.
(Litigation compensation was added as X-rays are frequently required in Worker’s Compensation asserts.) 90% of people with acute back pain will feel better if an X-ray and other tests are postponed for a month if none of these symptoms are present.
CT Or MRI Scan:
An MRI or CT scan may be necessary if you observe any warning signs of an infection, a fracture, or a more serious condition.
Imaging is also required if symptoms persist for more than a month and surgery is being considered. Obtaining imaging that goes beyond a straightforward X-ray is reasonable when a patient has already undergone back surgery.
If a patient exhibits symptoms of cauda equine syndrome, a serious spinal cord injury that results in symptoms including leg weakness, perineal numbness (numbness between the inner thighs), and difficulty peeing
This syndrome may lead to lifelong neurological damage (Lear all about Nerve Pain) if left untreated. A CT scan or, at the very least, an MRI is urgently required if there are any indications of this illness.
What Is Best Treatment Of Back Pain?
The most sense to try something other than a pill for back pain alleviation because medications frequently have short-lived and minimal benefits. The particulars vary according to the kind and severity of back pain.
Try these for short-term relief from low back pain:
- Spinal manipulation with acupuncture and heat therapy, similar to chiropractic care.
- An NSAID like ibuprofen 200mg & ibuprofen 400mg or naproxen or a muscle relaxant are viable options if these don’t work.
- Remedies for chronic low back pain:
- Exercise (including mobility, balance training, and strengthening of the core muscles).
- Programs based on mindfulness and physical therapy that aim to manage or lessen stress.
What’s The Best Way to Prevent Back Pain?
By strengthening your back with workouts and avoiding activities that can injure your back, you can help prevent some types of back pain.
The most effective treatment against back pain is movement and medication like, Aspadol er 200mg. Regular exercise can strengthen the back and prevent further pain occurrences.
Exercises should emphasize strengthening range of motion and strength on both sides of the body while also maintaining balance, as some back problems can begin when one side of the body is stronger than the other.
Additionally, avoid spending too much time sitting down. Sit at your desk in the office all day, but get up and move about at least once every 30 minutes.
What are the red flags to rule out for back pain?
If the pain lasts for four weeks or more. If the feeling of discomfort keeps getting worse over time.
If you have additional symptoms, such as a fever, significant weight loss or gain, weakness or lack of function in your extremities, bladder issues, etc.
How long is normal for back pain?
Back pain that is acute (short-term) may last for a few days to a few weeks. With self-care, it typically goes away on its own in a few days without a permanent loss of function.
Even after an original injury or primary cause of back pain has been treated, chronic back pain is pain that lasts for 12 weeks or more. Click to learn about: Thigh Pain | Finger Pain | Shoulder Pain
Can gas cause back pain?
Yes. Lower back pain from gas pain in the belly can also be felt, as can upper back pain from gas pain in the stomach. Our digestive systems naturally produce some gas, which many people pass up to 20 times each day.
What are the 4 stages of back pain?
These four stages are:
- Dysfunction Stage,
- The Dehydration Stage,
- The Stabilization Stage, and
- Collapsing Stage.
Can stress cause back pain?
Stress affects the body in a variety of ways, from mood swings and headaches to weight fluctuations. However, an often overlooked side effect of stress is neck and back pain. Over time, repetitive bouts of stress can cause musculoskeletal issues in these regions of the body.
What causes extremely tight back muscles?
Common causes of tense muscles include trauma, overuse or repetitive stress, and poor posture.
A sudden traumatic injury from lifting improperly, a fall or an accident, sometimes referred to as “throwing out your back,” typically leads to pain, inflammation and muscle spasms.