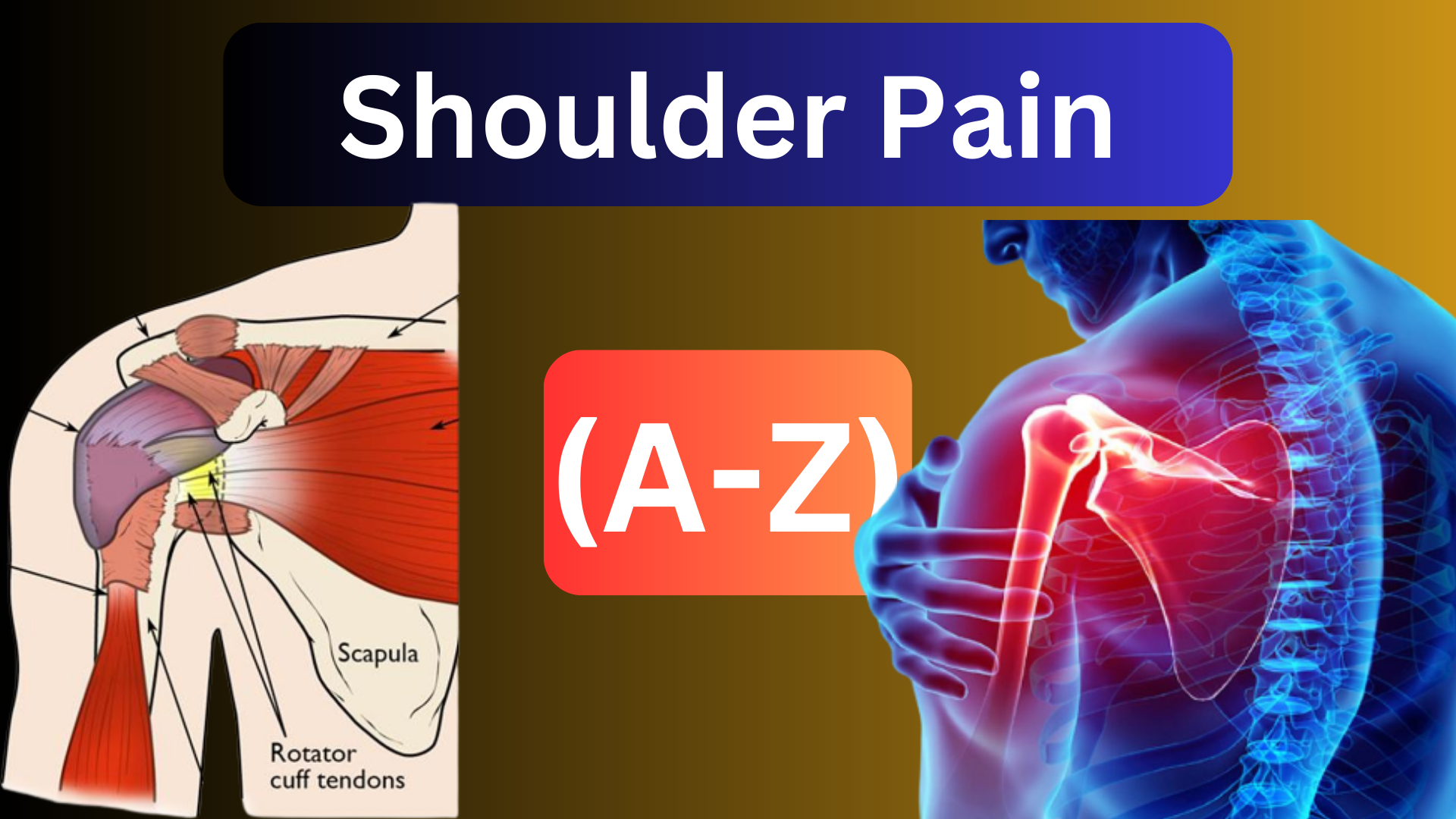
The muscles and tendons that make up the rotator cuff are connected to the bones in your shoulder joint and become the cause for shoulder pain. The group preserves your shoulder’s stability while allowing it to move.
When rotator cuff tendons get inflamed or stuck in your shoulder, this is the most frequent cause of shoulder pain.
Intense shoulder discomfort can also result from a rotator cuff tear, which happens when one of the tendons is ruptured due to abuse or an accident.
What is Shoulder Pain Actually?
Any kind of pain in or near the shoulder joint (Click to learn joint pain) is referred to as shoulder pain. Shoulder pain symptoms might range from a minor discomfort that gradually gets worse over a few weeks to a more serious, sudden agony.
Your shoulder’s rotator cuff may swell, sustain damage, or experience bone changes that result in pain that interferes with your daily tasks. Let’s discuss shoulder discomfort.
What are the Main Causes for Shoulder Pain?
When rotator cuff tendons get caught under the shoulder’s bony area, shoulder pain is often the result. The tendons swell up or suffer damage. It is also known as bursitis or tendinitis of the rotator cuff.
These are typical reasons for shoulder pain:
- As people age, arthritis, or joint inflammation, which causes pain and stiffness, develops.
- Fractures of the bones, such as those in the arm, shoulder, or collarbone.
- Bursitis, or swelling of the fluid-filled sacs that surround and safeguard joints.
- Overuse injuries that result in torn tendons or tendinitis, like a torn rotator cuff, can inflame the affected area.
- Shoulder instability, often known as dislocation or separation.
- Shoulder pain from pinched nerves in the neck, which can occasionally radiate to the hand.
- One or more bone spurs on the ends of the bones that connect to your shoulder joints.
Symptoms of Shoulder Pain?
These are some symptoms of shoulder pain:
- Warmth or redness in your shoulder,
- Neck pain, arm pain, or back pain,
- When you move your arm, you feel a selecting, popping, or grinding sensation,
- Rigidity and weakening in the muscles.
- Only a small range of motion.
Treatment of Shoulder Pain?
Therapy usually includes rest, changing your routine, and physical therapy to help you gain shoulder flexibility and strength. Shoulder pain can be avoided with common sense methods like avoiding excessive exertion or engaging in activities you normally wouldn’t.
Medication Treatment:
To treat pain and inflammation, your doctor may prescribe medication like, pain o soma 500mg & Aspadol 100mg. If medication is prescribed to treat pain, it should only be taken in accordance with directions. To ease discomfort, your doctor can also suggest getting steroid or painkiller injections.
Surgery:
For some shoulder issues, surgery may be required. However, a large percentage of patients with shoulder pain will benefit from easy treatments like changing activities, relaxation, physical activity, and medication.
Exercise may not be helpful for all shoulder issues, including certain rotator cuff injuries and recurrent dislocations. Surgery may be advised rather soon in these situations.
Prevention From Shoulder Pain?
Accidental injuries are not always preventable, but there are steps you can take to lessen your risk and safeguard your shoulder, like:
- When doing something, pay attention to your body’s signals; if something hurts, stop doing it until you feel stronger.
- Before doing any exercise, especially ones that require throwing or hanging from your arms, warm up.
- Continually exercise and maintain a healthy weight, as advised by your doctor.
- Exercises to build up the muscles around your shoulder should be done if your doctor suggests them to protect the joint.
- To support your shoulder and prevent repetitive use injuries at work, utilize correct ergonomics.
FAQs for Shoulder Pain –
What are red flags for shoulder pain?
If any indications of danger are found due to your shoulder pain then, it is urgent. And it is described as red flags for shoulder pain.
What is bursitis in the shoulder?
Tiny cavities filled with fluid called bursae serve to lessen friction between moving parts in your joints. Bursa in your shoulder, which is depicted in blue, can become inflamed or irritated if you have shoulder bursitis.
Does shoulder pain mean heart trouble?
Shoulder pain from heart disease can come from many of different places. Although a heart attack is most likely the condition with which this pain is most frequently associated, other possible cardiac conditions may also be to blame.
Where is rotator cuff pain felt?
Typically, you will have pain that travels from the front of your shoulder down the side of your arm.
It might be present when lifting or reaching overhead (such as when playing tennis or painting a ceiling). When you plan to fall asleep on the affected side, you might experience pain.
Can shoulder pain be a symptom of something else?
Arthritis in the shoulder joint is another potential cause of shoulder pain. Bone development near the shoulder. Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, a fluid-filled sac that normally pillows the joint and allows smooth movement.
How long should it take for shoulder pain to go away?
Mild shoulder pain may require between four and six weeks to completely resolve. To get rid of shoulder discomfort, there are some things you need to do and shouldn’t do.
What are 2 warning signs of a rotator cuff tear?
- Difficulties and discomfort brought on merely raising your arm.
- When you move your arm, you might hear or feel popping or clicking.
- Shoulder ache that gets worse at night or while your arm is at rest.
- Weakness in the shoulders and difficulty lifting objects.
What does a torn shoulder muscle feel like?
Deep in the shoulder, there is often a dull pain related to rotator cuff issues. It can happen as a result of particular motions like lifting or lowering the arm.
Some folks also feel unpleasant while they’re sleeping. Pain frequently keeps people up at night, especially if they are laying on the injured shoulder.

1 Comment